
High incidence of oral cancer in India is attributes to a number of etiological factors. The common causes for oral cancer are tobacco consumption habit either as smokeless tobacco or smoking and alcohol consumption. Positive family history of oral cancer, Viral infections like HPV, poor oral hygiene are the other causes for oral cancer. Based on the TMN classification , 48% of the oral cancer cases are diagnosed in the later stages.
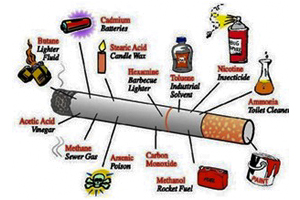
Estimates indicate 57% of men and 11% of women between 15- 49 years of age use some form of tobacco. More than 90% of oral cancer patients report using tobacco products in the form of smokeless tobacco- betel nut, pan (pieces of Areca nut), slaked lime, nut wrapped in piper betel vine leaf. Additionally gutka, panparag, zarda, mawa, kharra and khaini. Women chewing tobacco 10 or more times a day have a risk of 9.2 times that of non-tobacco chewers, irrespective of age of initiation of tobacco chewing.

Smoking includes cigarettes, bidi and hookah. These tobacco products are commercially available in sachets & it is very popular among young adults. Bidi smokers are 4 times at risk of developing oral cancer compared to non-smokers.


As per a study, more than 85% of oral cancer patients had poor oral hygiene. Poor oral hygiene related attributable risk is around 32% for men and 64% for women in India. It is an oral cancer risk to be wearing dentures for more than 15 years and not visiting a dentist regularly.
As per a study, more than 85% of oral cancer patients had poor oral hygiene. Poor oral hygiene related attributable risk is around 32% for men and 64% for women in India. It is an oral cancer risk to be wearing dentures for more than 15 years and not visiting a dentist regularly.
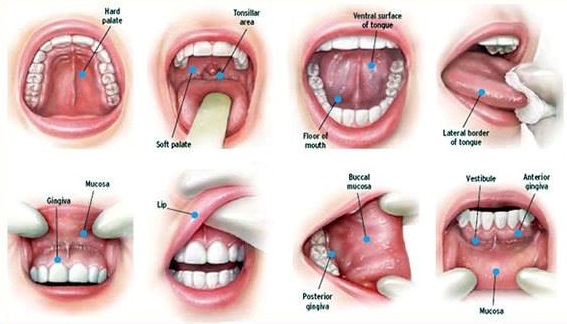
Oral cancer will remain a major health problem and the incidence will increase by 2020 and 2030 in both sexes, however early detection and prevention will reduce this burden. Oral cavity is accessible for visual examination, and oral cancers and premalignant lesions have well defined clinical diagnostic features but oral cancers are typically detected in their advanced stages. Oral cancer can be diagnosed earlier by self mouth examination and this increases awareness in high-risk communities.
The enforcement of laws on youth access to tobacco and alcohol; the prohibition of all advertising and promotional activities by the tobacco industry -the prominent inclusion of strong pictorial warnings in existing written warnings on the labels of tobacco and alcohol products are effective ways to prevent oral cancer. The role of HPV should be tackled in culturally acceptable health programs promoting safe sexual practices
People less than 40 years who are habitual cigarette smokers, alcohol consumers, and betel quid chewers must undergo oral mucosa screening regularly so that oral cancer can be identified as early as possible.